 gitsilence 的个人博客
gitsilence 的个人博客
Coding...
Spring Bean 的生命周期

Spring Bean 的生命周期
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean
在这个方法内打上 debug 断点,可以看到 IDEA 上的调用链
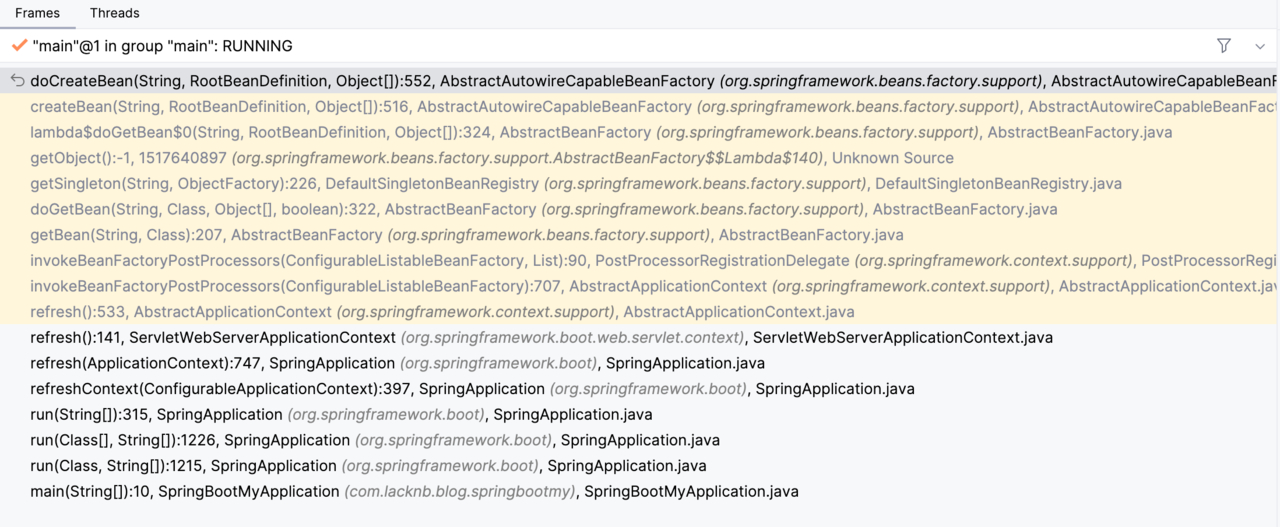
通过一点一点向上打断点,可以找到
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
通过这个方法,由于当前应用已经确定是 SERVLET, contextClass 对应的值是 org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
然后就是通过反射进行实例化
通过无参构造,调用了父类的无参构造方法,创建了 BeanFactory 的实例
public GenericApplicationContext() {
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}
==// TODO==
实例化
-
创建 Bean 实例
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBeanInstance -
设置属性值,Spring 容器注入必要的属性到 Bean 中
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#populateBean -
检查 Aware
如果 Bean 实现了 BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware 等这些 Aware 接口,Spring 容器会调用它们。
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBeanif (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); return null; }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); }private void invokeAwareMethods(String beanName, Object bean) { if (bean instanceof Aware) { if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) { ((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName); } if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) { ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader(); if (bcl != null) { ((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl); } } if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) { ((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this); } } } -
调用 BeanPostProcessor 的前置处理方法
在 Bean 初始化之前,允许自定义的 BeanPostProcessor 对实例进行处理,如修改 Bean 的状态,BeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessorsBeforeInitialization 方法此时会被调用。
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization@Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null) { return result; } result = current; } return result; }
初始化
-
调用 InitializingBean 的 afterPropertiesSet 方法。
提供一个机会,在所有 Bean 属性设置完毕后进行初始化操作。如果出现了Bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,afterPropertiesSet 方法会被调用。
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#invokeInitMethodsboolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean); if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'"); } if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { try { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> { ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); return null; }, getAccessControlContext()); } catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) { throw pae.getException(); } } else { ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); } } -
调用自定义 init-method 方法
提供一种配置方式,在 XML 配置中指定 Bean 的初始化方法。如果 Bean 在配置文件中定义了初始化方法,那么该方法会被调用。
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#invokeInitMethodsif (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) { String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName(); if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) && !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) { invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd); } }检查
initMethodName是否不为空(StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName)),并且不是标准的InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet方法("afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)),同时确保这个方法不是由外部管理的(mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName))。这些检查确保了只有用户自定义的初始化方法才会被调用。
-
调用 BeanPostProcessor 的后置处理方法
在 Bean 初始化之后,再次允许 BeanPostProcessor 对 Bean 进行处理。BeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessorsAfterInitialization 方法会在此时被调用。
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization@Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null) { return result; } result = current; } return result; }
注册 Destruction 回调
-
注册 Destruction 回调
如果 Bean 实现了 DisposableBean 接口或者在 Bean 中定义了自定义的销毁方法,Spring 容器会为这些 Bean 注册一个销毁回调,确保在容器关闭时能够正确清理资源。
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#registerDisposableBeanIfNecessaryprotected void registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { AccessControlContext acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null ? getAccessControlContext() : null); if (!mbd.isPrototype() && requiresDestruction(bean, mbd)) { if (mbd.isSingleton()) { // Register a DisposableBean implementation that performs all destruction // work for the given bean: DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors, // DisposableBean interface, custom destroy method. // 用于将给定的Bean名称和DisposableBean实例注册到容器中。这样,当容器关闭时,这些Bean将被自动销毁。 // 当容器关闭时,DisposableBeanAdapter的destroy方法将被调用。这个方法首先会应用所有的BeanPostProcessor,然后调用DisposableBean的destroy方法或者通过反射调用在BeanDefinition中指定的销毁方法。 registerDisposableBean(beanName, new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc)); } else { // A bean with a custom scope... Scope scope = this.scopes.get(mbd.getScope()); if (scope == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + mbd.getScope() + "'"); } scope.registerDestructionCallback(beanName, new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc)); } } }
Bean 的正常使用
- 到此,Bean 已经完全初始化,可以开始处理应用程序的请求了。
Bean 的销毁
-
调用 DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessorBeforeDestruction 方法
创建 DisposableBeanAdapter 的时候,通过传的 postProcessors 筛选出 DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
-
调用 DisposableBean 的 destroy 方法
当容器关闭时,如果 Bean 实现了 DisposableBean 接口,destroy 方法将会被调用。
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DisposableBeanAdapter#destroyif (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> { ((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy(); return null; }, this.acc); } else { ((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy(); } -
调用自定义的 destroy-method
如果 Bean 在配置文件中配置了销毁方法,那么该方法会被调用。
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DisposableBeanAdapter#destroyif (this.destroyMethod != null) { invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod); } else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) { Method methodToInvoke = determineDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethodName); if (methodToInvoke != null) { invokeCustomDestroyMethod(ClassUtils.getInterfaceMethodIfPossible(methodToInvoke)); } }
最后
总结一下:
创建实例、
属性填充、
检查Aware、
执行 postProcessorsBeforeInitialization 方法、
执行 InitializingBean 的 afterPropertiesSet 方法、
执行自定义 init 方法、
执行 postProcessorsAfterInitialization 方法、
注册 Destruction 回调、
执行销毁方法(DisposableBeanAdapter)、
执行自定义的销毁方法
文本内容摘抄自 Hollis 八股文。